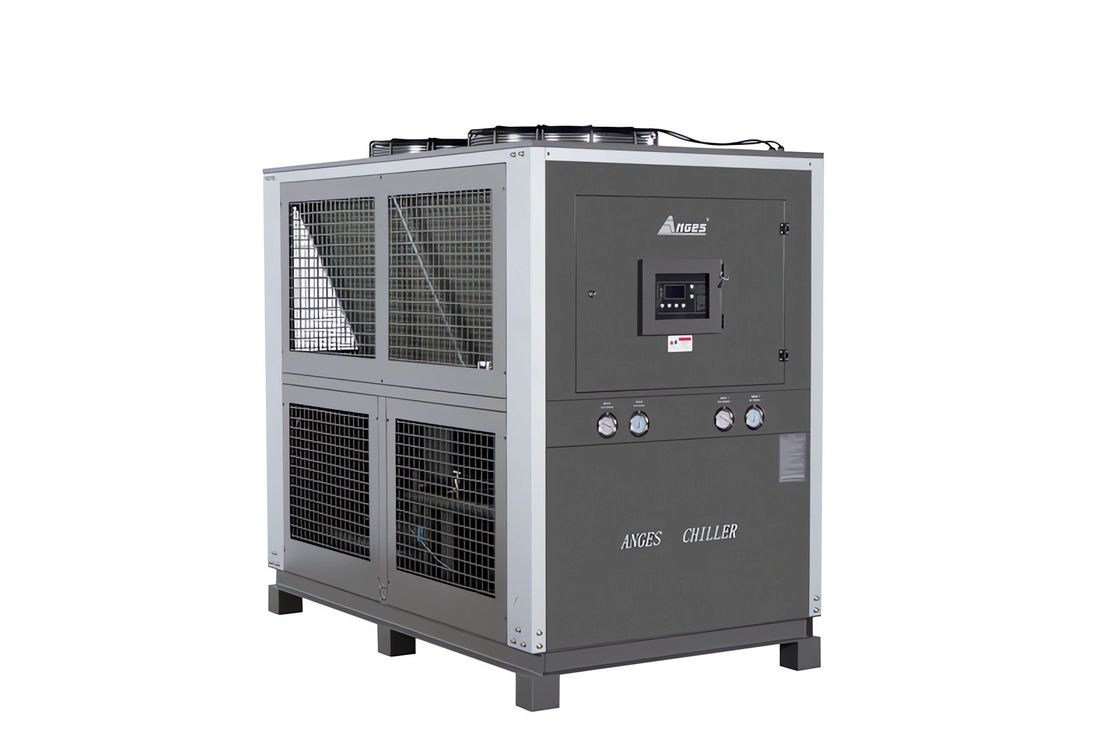
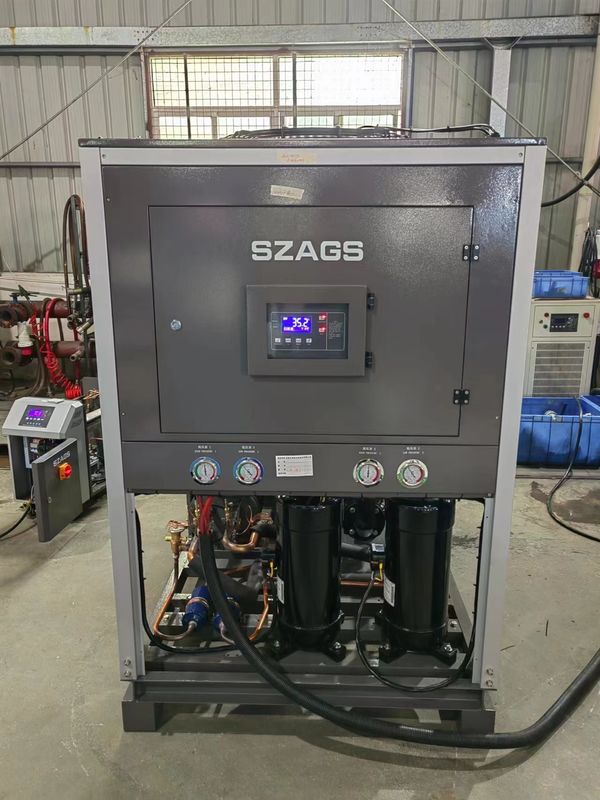
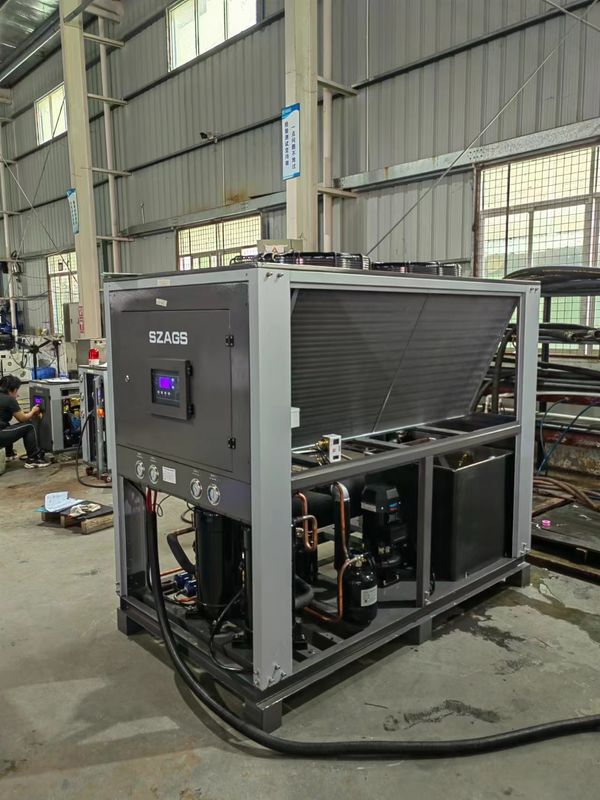
20HP Air Cooled Cooling System Industrial Air Cooled Scroll Type Water Chiller
The benefits of using chiller:
-
Efficient Cooling: Chillers deliver reliable and consistent cooling, maintaining stable operating temperatures for a wide range of industrial processes and equipment.
-
Energy Efficiency: Equipped with advanced energy-saving technologies, modern chillers minimize energy consumption and reduce operating costs.
-
Precise Process Control: With accurate temperature regulation, chillers ensure optimal conditions for specific applications, enhancing product quality and uniformity.
-
Equipment Longevity: By managing temperatures effectively, chillers protect sensitive equipment from overheating and damage, extending its lifespan and lowering maintenance needs.
-
Eco-Friendly Solutions: Utilizing refrigerants with low environmental impact, chillers support sustainability by reducing greenhouse gas emissions and limiting ozone depletion.
How to select the model of the chiller?
1. Determine Cooling Load:
Calculate the required cooling load for your application, expressed in tons of refrigeration (TR) or kilowatts (kW). Account for factors such as space size, heat generated by equipment, and external environmental conditions.
2. Type of Chiller:
- Air-cooled chillers: Ideal for smaller applications, easy to install and maintain.
- Water-cooled chillers: More efficient for larger applications but require cooling towers, additional space, and higher maintenance.
3. Application and Environment:
Evaluate whether the chiller is intended for industrial processes, comfort cooling, or other applications. Consider the ambient temperature and environmental conditions at the installation site.
4. Energy Efficiency:
Select chillers with a high Coefficient of Performance (COP) or Energy Efficiency Ratio (EER). Models with variable speed drives (VSD) can optimize energy usage and improve efficiency.
5. Capacity Control:
Ensure the chiller can adjust its capacity to meet varying cooling loads. This feature enhances energy savings and overall efficiency.
6. Size and Footprint:
Confirm that the chiller’s size and footprint align with the available installation space.
7. Initial and Operating Costs:
Weigh the initial purchase price against long-term operating costs, including energy use and maintenance. Evaluate the total cost of ownership over the equipment’s lifespan.
8. Reliability and Maintenance:
Choose a chiller known for reliability and ease of maintenance. Check for good service support and the availability of spare parts.
9. Regulatory Compliance:
Verify that the chiller adheres to local regulations and standards, particularly those concerning environmental impact.
10. Manufacturer and Warranty:
Opt for reputable manufacturers that offer robust after-sales service, support, and comprehensive warranties.
By considering these factors and following these steps, you can select a chiller model that is efficient, reliable, and suitable for your specific application.
Specification
|
Model
Item
|
ACK-20(D) |
| nominal cooling capacity |
kcal/h |
51772 |
| kw |
60.2 |
| input power |
kw |
19.96 |
| power supply |
3PH 380V 50HZ |
| refrigerant |
type |
R407C |
| type of control |
thermostatic expansion valve |
| compressor |
type |
hermetic scroll |
| power(kw) |
16.2 |
| condenser |
type |
finned copper tube + low noise outer rotor fan |
| cooling air flow(m3/h) |
20000 |
| evaporator |
type |
shell and tube |
| chilled fluid flow(m3/h) |
10.38 |
| volume(L) |
170 |
| inlet and outlet pipe diameter(inch) |
2 |
| pump |
power(kw) |
2.2 |
| lift(m) |
20 |
| safety protection |
compressor overheating protection, over-current protection, high and low pressure protection, over-temperature protection,flow switch protection, phase sequence or missing phase protection, exhaust overheating protection |
| weight |
kg |
950 |
| dimension |
mm |
2000*1130*1820 |
Note: The nominal cooling capacity is according to: Inlet chilled fluid temperature: 17℃,outlet chilled fluid temperature: 12℃.
FAQ
1.How does a chiller system work?
The chiller operates with two circulations: one involves the circulation of process water, while the other entails the circulation of refrigerant gas. Heat absorbed from the process is transferred to the refrigerant circulation, and then expelled to either air or water.
2.How to calculate cooling capacity for chillers?
Cooling Capacity(kw)= Flow Rate(m3/h)*Temp Change(T1-t2)/0.86
Heat Load= C(specific heat)* M(quality output per hour )*Temp Change(T1-T2)
3.How can we do for chiller maintenance?
Examining the temperature of the chilled water upon entry and exit from the chiller system is essential.
Examine and confirm the temperature of the condenser water upon entry and exit from the system.
Inspect the power consumption and current of the compressor.
Examine the level and temperature of the oil in the oil sump.
Inspect the pressures of both the condenser and evaporator.
Verify and document the readings of the oil pressure.
Inspect the chiller system for any unusual noise or vibration.
4. What kind of after-sales service can we provide?
24 hours Online support;
Video technical support;
Overseas third-party support available and etc.

 Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!  Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail! 



